Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behavior. Psychologists are actively involved in studying and understanding mental processes, brain functions, and behavior. The field of psychology is considered as “Hub Science” with strong connections to the medical sciences, social sciences, and education. Take Pritish Kumar’s Guidance, you can truly get informative knowledge about psychology.

Fast facts about psychology
- Psychology is the study of behavior and the mind.
- There are different types of psychology, such as cognitive, forensic, social, and developmental psychology.
- A person with a condition that affects their mental health may benefit from assessment and treatment with a psychologist.
- A psychologist may offer treatment that focuses on behavioral adaptations.
- A psychiatrist is a medical doctor who is more likely to focus on medical management of mental health issues.
What is psychology?
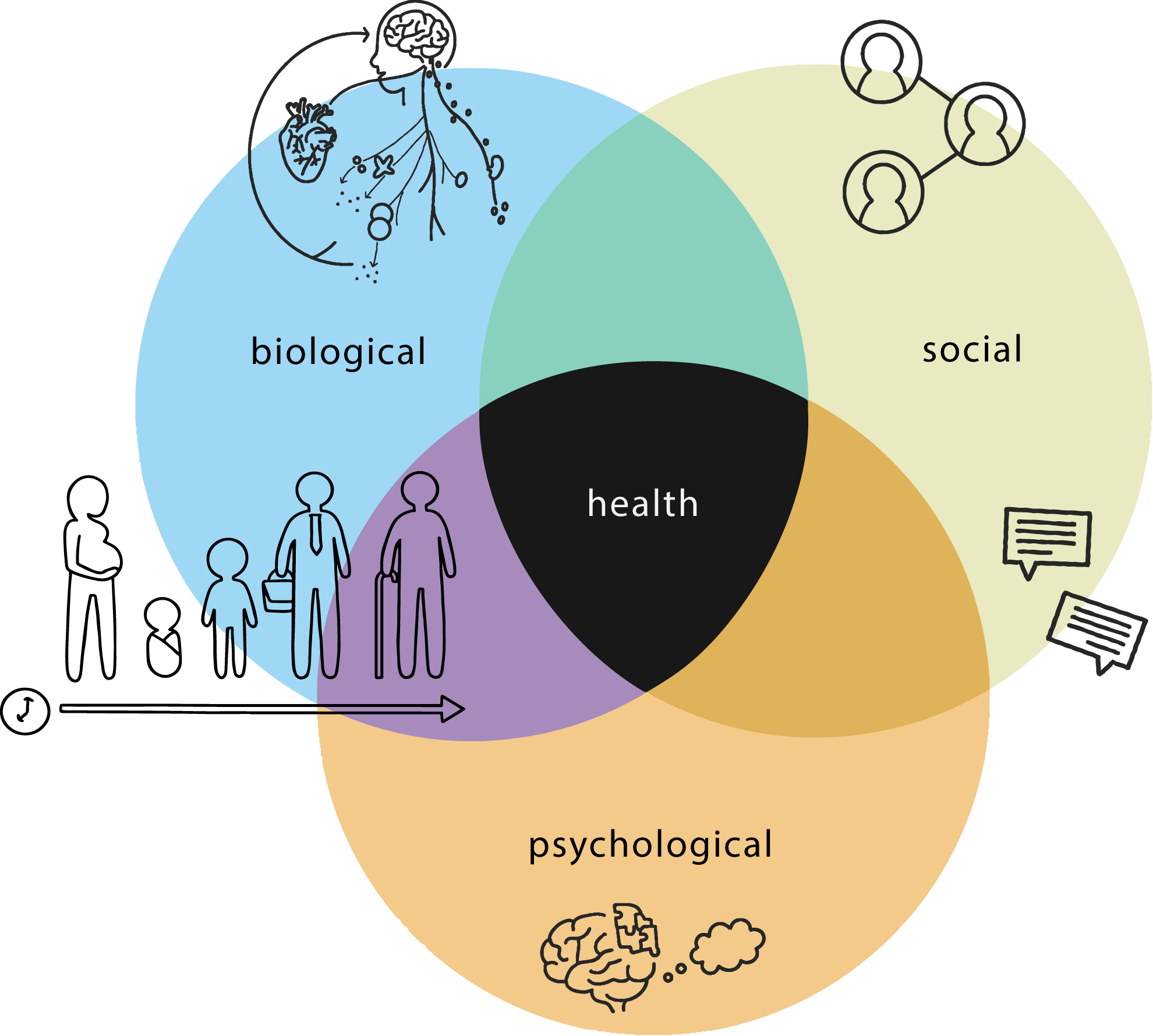
The mind is highly complex, and conditions that relate to it can be hard to treat. Thought processes, emotions, memories, dreams, perceptions, and so on cannot be seen physically, like a skin rash or heart defect. While physical signs of some mental health issues can be observed, such as the plaques that develop with Alzheimer’s disease, many theories of psychology are based on observation of human behavior.
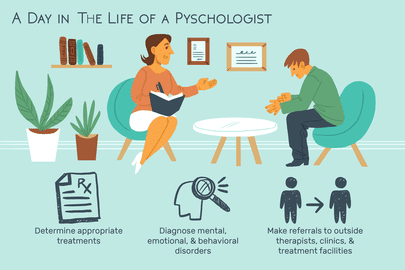
Practicing psychologist
A practicing psychologist will meet with patients, carry out assessments to find out what their concerns are and what is causing any difficulties, and recommend or provide treatment, for example, through counseling and psychotherapy.
:strip_icc()/psychologist-526059-Final-9386324d0b70411f8320ff5bdde11e1d.png)
Roles of a psychologist
Psychologists may have other roles, too. They carry out studies to advise health authorities and other bodies on social and other strategies, assess children who find it difficult to learn in school, give workshops on how to prevent bullying, work with recruitment teams in companies, and much more.
Branches of psychology
There are different types of psychology that serve different purposes. There is no fixed way of classifying them,
Here are some common types:
/The-Major-Branches-of-Psychology-4139786-final-15133a69be64406db16dc63cd97a3a17.png)
Clinical psychology
Clinical psychology integrates science, theory, and practice in order to understand, predict and relieve problems with adjustment, disability, and discomfort. It promotes adaption, adjustment, and personal development.
A clinical psychologist concentrates on the intellectual, emotional, biological, psychological, social, and behavioral aspects of human performance throughout a person’s life, across varying cultures and socioeconomic levels.
Cognitive psychology
Cognitive psychology investigates internal mental processes, such as problem solving, memory, learning, and language. It looks at how people think, perceive, communicate, remember, and learn. It is closely related to neuroscience, philosophy, and linguistics.
Developmental psychology
This is the scientific study of systematic psychological changes that a person experience over the life span, often referred to as human development. It priorities not only on infants and young children but also teenagers, adults, and older people. Factors include motor skills, problem solving, moral understanding, acquiring language, emotions, personality, self-concept, and identity formation.
Evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology looks at how human behavior, for example language, has been affected by psychological adjustments during evolution. An evolutionary psychologist believes that many human psychological traits are adaptive in that they have enabled us to survive over thousands of years.
Forensic psychology
Forensic psychology involves applying psychology to criminal investigation and the law. A forensic psychologist practices psychology as a science within the criminal justice system and civil courts. It involves assessing the psychological factors that might influence a case or behavior and presenting the findings in court.
Health psychology
Health psychology is also called behavioral medicine or medical psychology. It observes how behavior, biology, and social context influence illness and health. A physician often looks first at the biological causes of a disease, but a health psychologist will focus on the whole person and what influences their health status. This may include their socioeconomic status, education, and background, and behaviors that may have an impact on the disease, such as compliance with instructions and medication.
Neuropsychology
Neuropsychology looks at the structure and function of the brain in relation to behaviors and psychological processes. A neuropsychology may be involved if a condition involves lesions in the brain, and assessments that involve recording electrical activity in the brain. A neuropsychological evaluation is used to determine whether a person is likely to experience behavioral problems following suspected or diagnosed brain injury, such as a stroke
Occupational psychology
Occupational or organizational psychologists are involved to assess and to make recommendations about the performance of people at work and in training. They help companies to find more effective ways to function, and to understand how people and groups behave at work. This information can help improve effectiveness, efficiency, job satisfaction, and employee retention.
Social psychology
Social psychology uses scientific methods to understand how social influence impact human behavior. It seeks to explain how feelings, behavior, and thoughts are influenced by the actual, imagined or implied presence of other people.
A social psychologist looks at group behavior, social perception, non-verbal behavior, conformity, aggression, prejudice, and leadership. Social perception and social interaction are seen as key to understanding social behavior.
Reference
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/154874#what-is-psychology