What Is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the lungs. Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. To learn more about how cancers start and spread, see What Is Cancer?
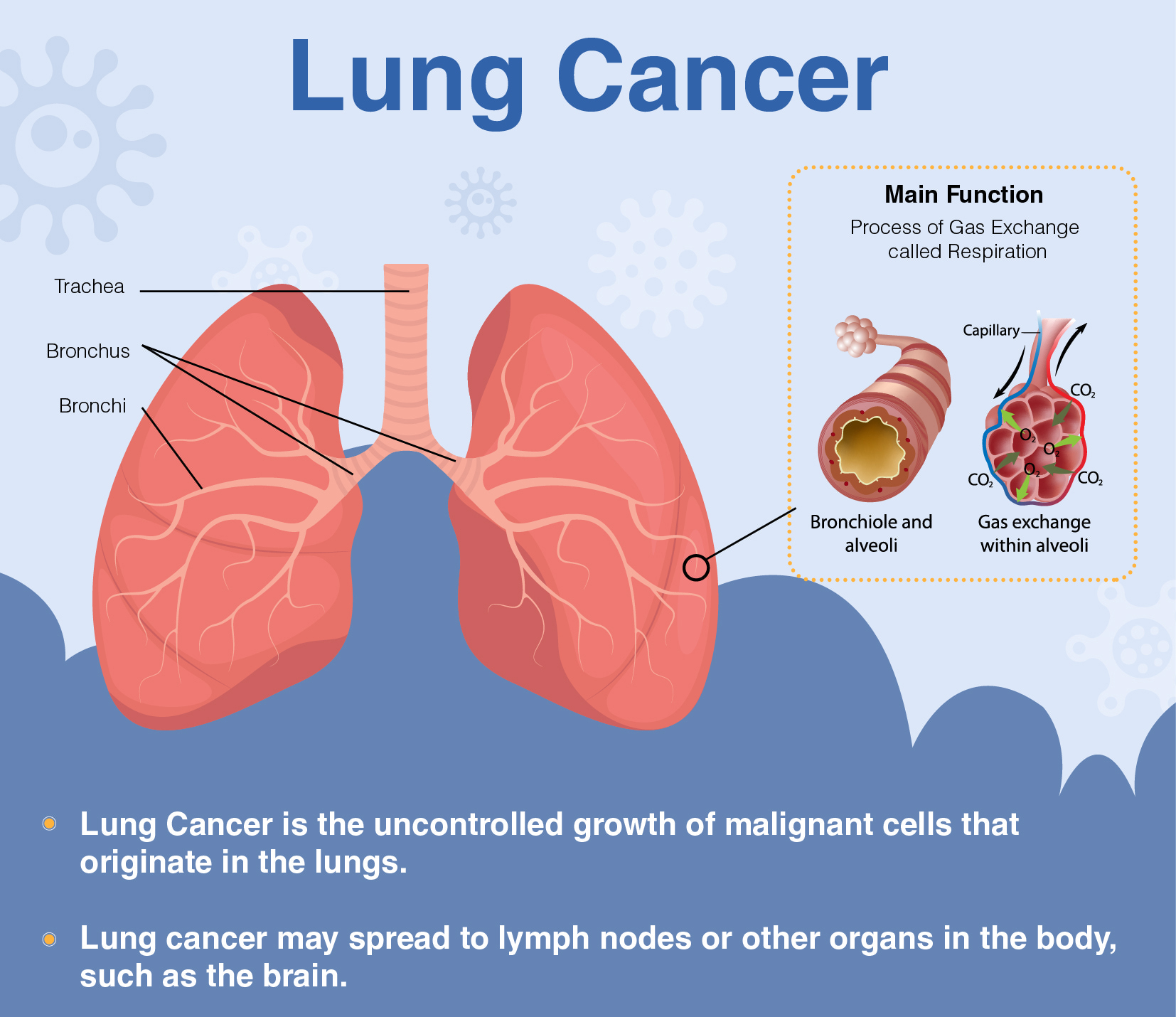
Normal structure and function of the lungs
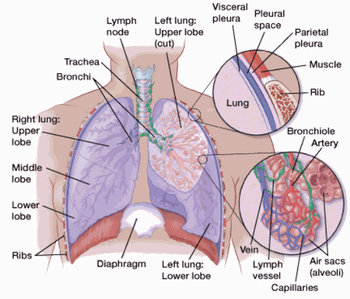
Your lungs are 2 sponge-like organs in your chest. Your right lung has 3 sections, called lobes. Your left lung has 2 lobes. The left lung is smaller because the heart takes up more room on that side of the body.
When you breathe in, air enters through your mouth or nose and goes into your lungs through the trachea (windpipe). The trachea divides into tubes called bronchi, which enter the lungs and divide into smaller bronchi. These divide to form smaller branches called bronchioles. At the end of the bronchioles are tiny air sacs known as alveoli.

The alveoli absorb oxygen into your blood from the inhaled air and remove carbon dioxide from the blood when you exhale. Taking in oxygen and getting rid of carbon dioxide are your lungs’ main functions. Lung cancers typically start in the cells lining the bronchi and parts of the lung such as the bronchioles or alveoli.
A thin lining layer called the pleura surrounds the lungs. The pleura protects your lungs and helps them slide back and forth against the chest wall as they expand and contract during breathing.
Below the lungs, a thin, dome-shaped muscle called the diaphragm separates the chest from the abdomen. When you breathe, the diaphragm moves up and down, forcing air in and out of the lungs.
Types of lung cancer
In this blog, Pritish Kumar Halder discusses common queries regarding lung cancer and its symptoms.
There are 2 main types of lung cancer and they are treated very differently.
Non-small cell lung cancer
About 80% to 85% of lung cancers are NSCLC. The main subtypes are adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. These subvariants, which start from different types of lung cells are grouped together as non-small cell because their treatment and prognoses (outlook) are often similar.

Adenocarcinoma:
It start in the cells that would normally secrete substances such as mucus.
This variant of cancer occurs mainly in people who currently smoke or formerly smoked, but it is also the most common type of lung cancer seen in people who don’t smoke. It is more common in women than in men, and it is more likely to occur in younger people than other types of lung cancer.
Adenocarcinoma is usually found in the outer parts of the lung and is more likely to be found before it has spread.
People with a type of adenocarcinoma called adenocarcinoma in situ (previously called bronchioloalveolar carcinoma) tend to have a better outlook than those with other types of lung cancer.
Squamous cell carcinoma:
Carcinomas start in squamous cells, which are flat cells that line the inside of the airways in the lungs. They are often linked to a history of smoking and tend to be found in the central part of the lungs, near a main airway (bronchus).
Large cell (undifferentiated) carcinoma
The cell can appear in any part of the lung. It tends to grow and spread quickly, which can make it harder to treat. A subtype of large cell carcinoma, known as large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, is a fast-growing cancer that is very similar to small cell lung cancer.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
About 10% to 15% of all lung cancers are SCLC and it is sometimes called oat cell cancer.
This type of lung cancer tends to grow and spread faster than NSCLC. About 70% of people with SCLC will have cancer that has already spread at the time they are diagnosed. Since this cancer grows quickly, it tends to respond well to chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Unfortunately, for most people, the cancer will return at some point.

Other types of lung tumors
Along with the main types of lung cancer, other tumors can occur in the lungs.
Lung carcinoid tumors:
Tumors of the lung account for fewer than 5% of lung tumors. Most of these grow slowly. For more information about these tumors, see Lung Carcinoid Tumor.
Other lung tumors:
Different cancer such as adenoid cystic carcinomas, lymphomas, and sarcomas, as well as benign lung tumors such as hamartomas are rare. These are treated differently from the more common lung cancers and are not discussed here.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/where-does-lung-cancer-spread-2249368_FINAL-5c45525e46e0fb00012e5e7d.png)
Cancers that spread to the lungs:
Signs that start in other organs (such as the breast, pancreas, kidney, or skin) can sometimes spread (metastasize) to the lungs, but these are not lung cancers. For example, cancer that starts in the breast and spreads to the lungs is still breast cancer, not lung cancer. Treatment for metastatic cancer to the lungs is based on where it started (the primary cancer site).
/lung-cancer-symptoms-4014389_color-9405196b97064d509fe43ef1f8f14e2d.gif)
Signs and Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Few lung cancers do not cause any symptoms until they have spread, but some people with early lung cancer do have symptoms. If you go to your doctor when you first notice symptoms, your cancer might be diagnosed at an earlier stage, when treatment is more likely to be effective.
Most of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than lung cancer. Still, if you have any of these problems, it’s important to see your doctor right away so the cause can be found and treated, if needed.

That most common symptoms of lung cancer are:
- A cough that does not go away or gets worse
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored sputum (spit or phlegm)
- Chest pain that is often worse with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing
- Hoarseness
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling tired or weak
- Infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia that don’t go away or keep coming back
- New onset of wheezing
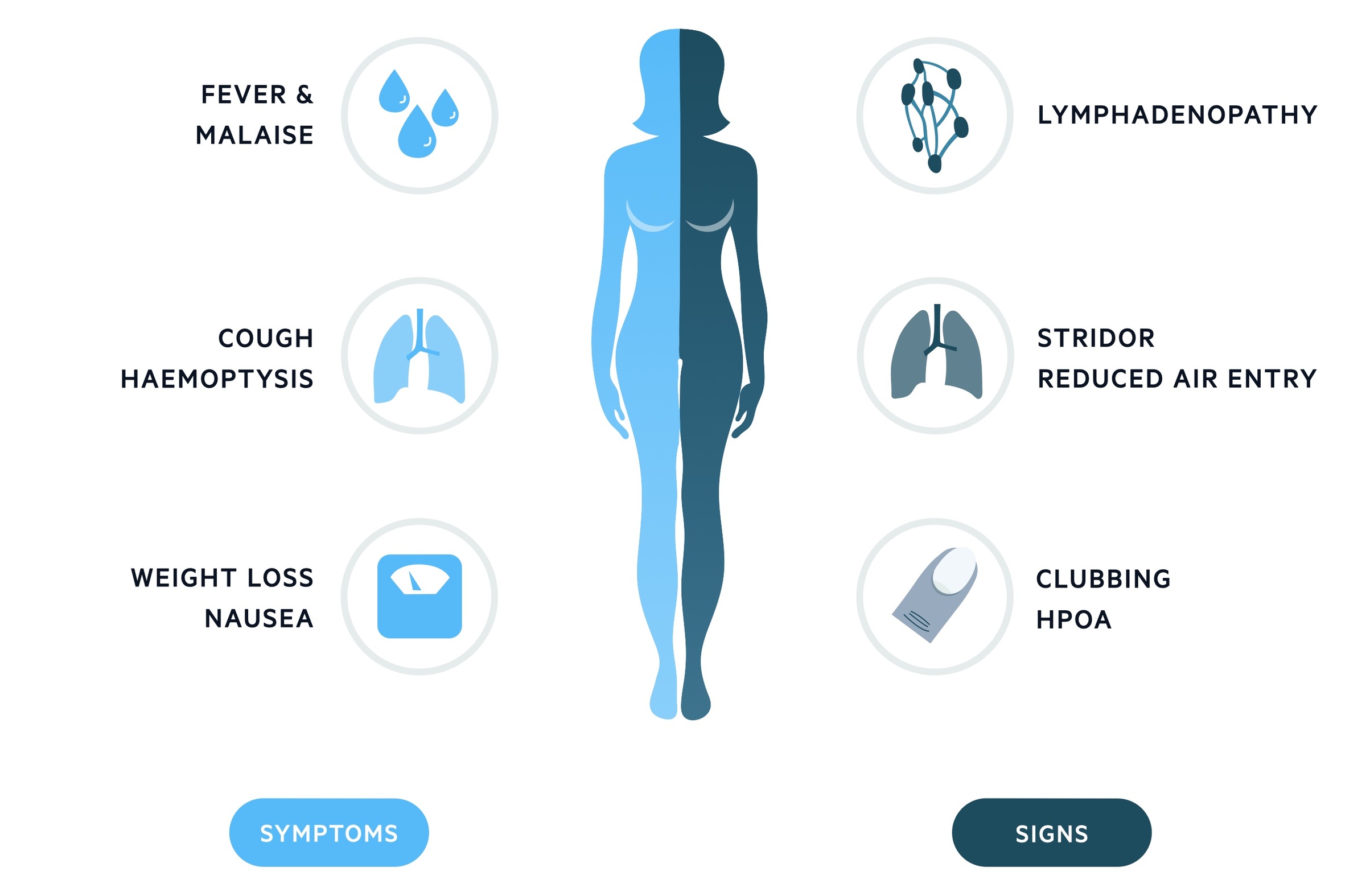
If lung cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it may cause:
- Bone pain (like pain in the back or hips)
- Nervous system changes (such as headache, weakness or numbness of an arm or leg, dizziness, balance problems, or seizures), from cancer spread to the brain
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice), from cancer spread to the liver
- Swelling of lymph nodes (collection of immune system cells) such as those in the neck or above the collarbone
Some lung cancers can cause syndromes, which are groups of specific symptoms.
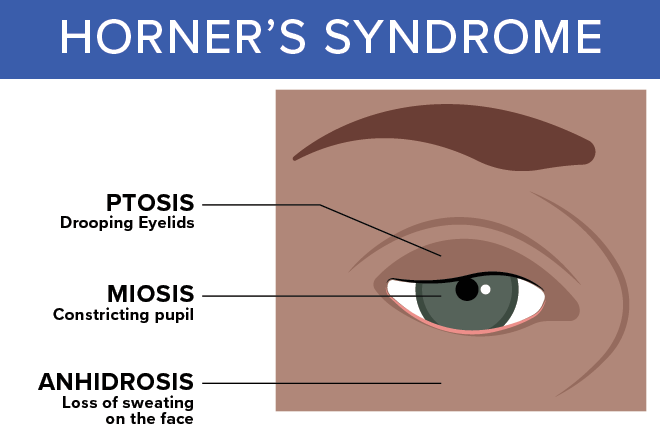
Horner syndrome
Cancers of the upper part of the lungs are sometimes called Pancoast tumors. These tumors are more likely to be non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) than small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Pancoast tumors can affect certain nerves to the eye and part of the face, causing a group of symptoms called Horner syndrome:
- Drooping or weakness of one upper eyelid
- A smaller pupil (dark part in the center of the eye) in the same eye
- Little or no sweating on the same side of the face
Pancoast tumors can also sometimes cause severe shoulder pain.

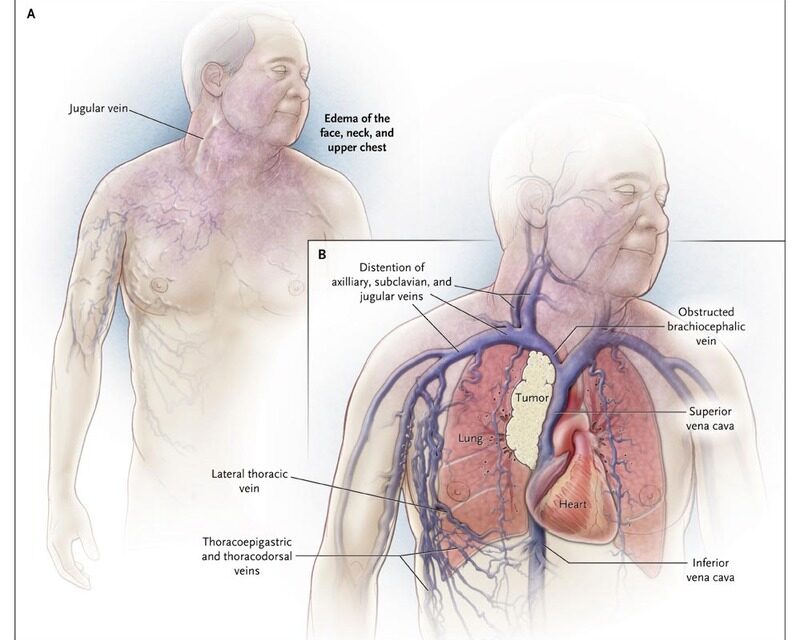
Superior vena cava syndrome
The superior vena cava (SVC) is a large vein that carries blood from the head and arms down to the heart. It passes next to the upper part of the right lung and the lymph nodes inside the chest. Tumors in this area can press on the SVC, which can cause the blood to back up in the veins. This can lead to swelling in the face, neck, arms, and upper chest (sometimes with a bluish-red skin color). It can also cause headaches, dizziness, and a change in consciousness if it affects the brain. While SVC syndrome can develop gradually over time, in some cases it can become life-threatening, and needs to be treated right away.
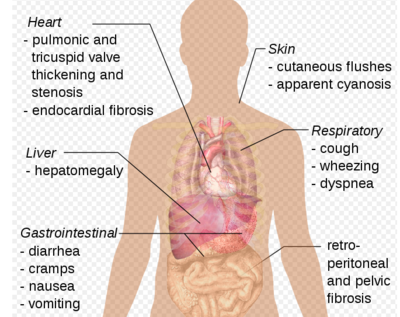
Paraneoplastic syndromes
Some lung cancers make hormone-like substances that enter the bloodstream and cause problems with distant tissues and organs, even though the cancer has not spread to those places. These problems are called paraneoplastic syndromes. Sometimes these syndromes may be the first symptoms of lung cancer. Because the symptoms affect other organs, a disease other than lung cancer may first be suspected as causing them.

Such syndrome can happen with any lung cancer but are more often associated with SCLC. Some common syndromes include:
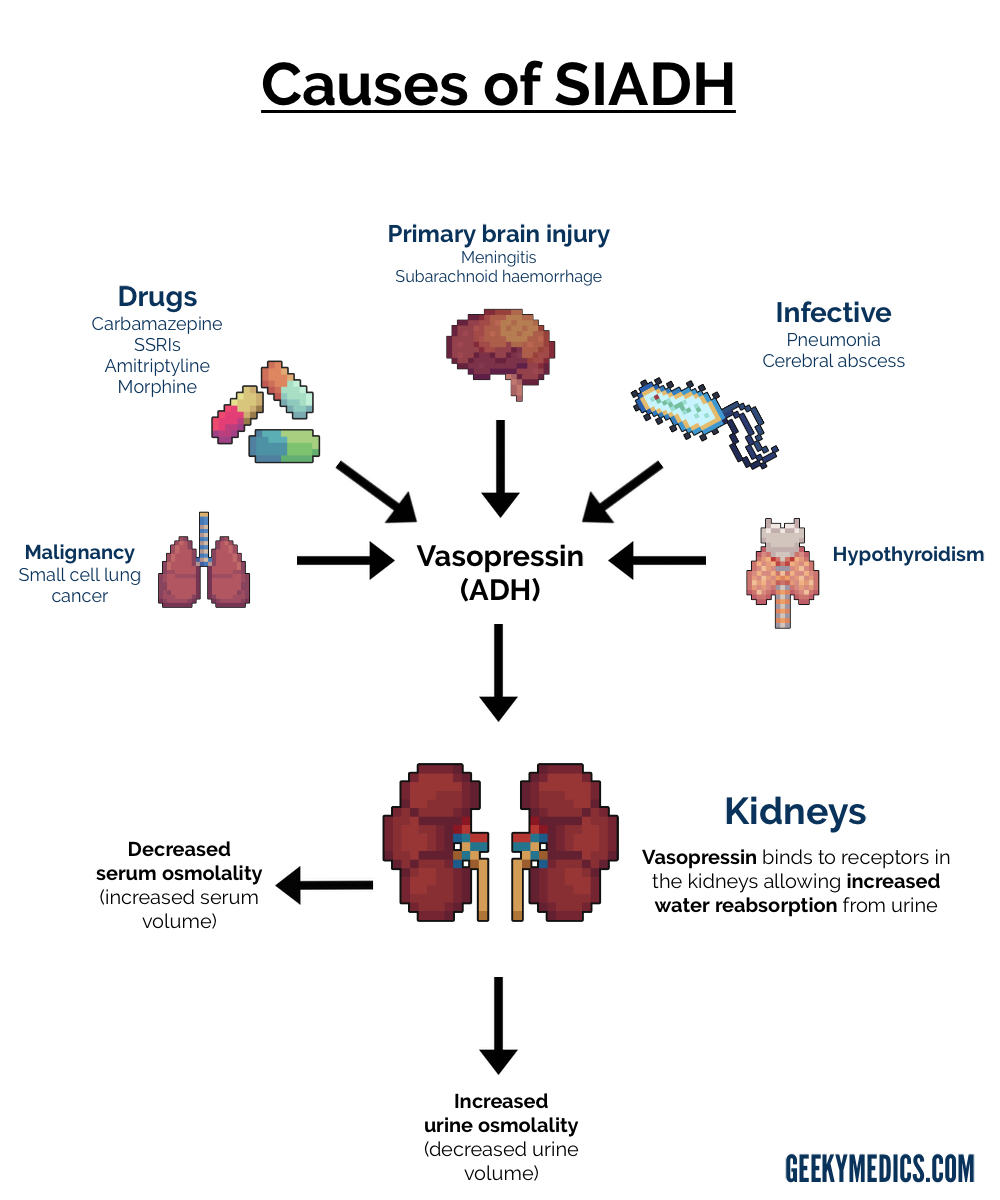
SIADH (syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone)
The cancer cells make ADH, a hormone that causes the kidneys to hold water. This lowers salt levels in the blood. Symptoms of SIADH can include fatigue, loss of appetite, muscle weakness or cramps, nausea, vomiting, restlessness, and confusion. Without treatment, severe cases may lead to seizures and coma.
Cushing syndrome
In this condition, the cancer cells make ACTH, a hormone that causes the adrenal glands to make cortisol. This can lead to symptoms such as weight gain, easy bruising, weakness, drowsiness, and fluid retention. Cushing syndrome can also cause high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, or even diabetes.

Nervous system problems
SCLC can sometimes cause the body’s immune system to attack parts of the nervous system, which can lead to problems. One example is a muscle disorder called Lambert-Eaton syndrome. In this syndrome, muscles around the hips become weak. One of the first signs may be trouble getting up from a sitting position. Later, muscles around the shoulder may become weak. A less common problem is paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration, which can cause loss of balance and unsteadiness in arm and leg movement, as well as trouble speaking or swallowing. SCLC can also cause other nervous system problems, such as muscle weakness, sensation changes, vision problems, or even changes in behavior.
High levels of calcium in the blood (hypercalcemia), which can cause frequent urination, thirst, constipation, nausea, vomiting, belly pain, weakness, fatigue, dizziness, and confusion

Blood clots
Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than lung cancer. Still, if you have any of these problems, it’s important to see your doctor right away so the cause can be found and treated, if needed.
Reference
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/signs-symptoms.html









Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!