In the intricate landscape of IT infrastructure, the paramount importance of sustaining data availability and seamless user access necessitates a closer look at backup domain controllers (BDCs). This blog delves into what BDCs are, their pivotal role in network redundancy, and why their integration should be a cornerstone of every organization’s IT strategy.
Understanding Backup Domain Controllers
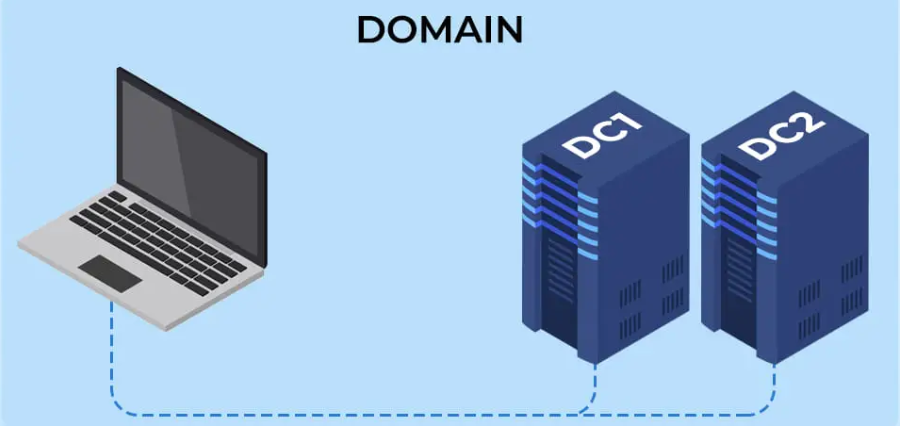
A backup domain controller (BDC) stands as a pivotal component in Microsoft Windows-based network environments. Collaborating with the primary domain controller (PDC), a BDC manages authentication requests, user accounts, and security policies. Crucially, BDCs replicate data and configurations from the PDC, ensuring redundancy and fault tolerance.
Significance of Backup Domain Controllers
Redundancy and High Availability: BDCs are instrumental in providing redundancy. In instances where the primary domain controller faces unavailability due to hardware issues or maintenance, BDCs seamlessly take over, guaranteeing uninterrupted user access to network resources.
Load Balancing: Distributing authentication load evenly across the network, BDCs prevent overwhelming the PDC or BDC, averting potential performance issues.
Faster Logins: In geographically distributed networks, the presence of multiple domain controllers allows users to authenticate against the nearest one, reducing latency and enhancing login speeds.
Improved Disaster Recovery: Offering flexibility in disaster recovery, BDCs can be promoted to PDC status in case of catastrophic PDC failure, simplifying recovery procedures and minimizing downtime.
Enhanced Security: BDCs contribute to distributing security policies and user account information, ensuring consistency in security configurations across the network.
Implementing Backup Domain Controllers
Efficient implementation involves:
Set Up BDCs: Deploy additional servers as BDCs in the network, aligned with the PDC’s operating system version.
Replication: Configure replication settings to synchronize crucial data regularly between the PDC and BDCs.
Monitoring and Maintenance: Regularly monitor BDC health and perform routine maintenance, including updates and backups.
Failover Testing: Periodically conduct failover tests to validate seamless BDC takeover in PDC unavailability scenarios.
While backup domain controllers may operate behind the scenes, their significance is undeniable. Acting as unsung heroes, BDCs contribute to redundancy, high availability, and load balancing, ensuring uninterrupted access to network resources. Strategically incorporating and maintaining BDCs fortifies an organization’s data availability and disaster recovery capabilities, fostering a resilient and robust IT environment.
—————————————————————————————–
Author Introduction: Pritish Kumar Halder
Pritish Kumar Halder, an adept real estate analyst, ventures into the intricate dynamics of IT infrastructure. With a knack for unraveling complexities, he strives to empower readers with valuable insights. Pritish excels in translating industry intricacies into digestible information, making IT concepts accessible to all.