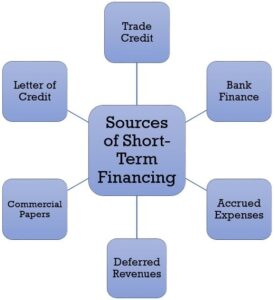
The short term means a period of less than one year. There are three main sources of short-term external finance: bank overdrafts, trade credit and debt factoring.
For more nformaion read Pritish Kumar Halder aticles.
Bank overdrafts
A bank overdraft is a negative balance on the business bank account. The bank agrees to allow a firm to overdraw its account up to an agreed maximum limit. This is the most flexible source of finance as the firm can increase or decrease the overdraft on a daily basis. Interest is payable on any overdrawn balance.
SOURCES OF SHORT TERM FINANCE
Overdrafts are a current liability (due to be repaid within a year).
- Interest is paid only on the amount by which the firm is overdrawn.
- Overdrafts are flexible – they can be paid off whenever the firm wishes.
- Interest rates on overdrafts are high.
- Some banks charge a flat rate fee for allowing an overdraft.
- Overdrafts should not be used for long-term financing.
Trade credit
Most transactions between firms are on a credit basis, where the purchasing firm is given time to pay for the items received, often three months. Choosing to delay paying for goods and services is a form of finance because the cash for the payment stays with the purchasing firm. Indeed, the firm may sell the item it bought on credit before actually paying for it.
Debt factoring
Firms keep records of money owing to them in a debtors book. Sometimes a firm raises finance by selling book at less than its face value to a factoring company. The advantage is that the firm gets immediate liquidity but loses a percentage of the value of its debts. The factoring company takes the risk of debts going ‘bad’.
Medium-term sources
The medium term is normally used to denote a one to five-year time period. There are two main sources of medium-term external finance: leasing and medium-term bank loans.
Leasing
A lease is a contract that allows a firm to rent an asset in return for regular payments. Leasing does not bring in money, but it allows a firm to gain use of expensive assets, e.g. machinery, without large cash payments. When the lease ends, the firm can update the equipment, as it is common in high-technology industries.
FIRMS PAYMENTS AND ASSETS
- Firms acquire expensive assets that would normally be unavailable. Failing to make payments results in the lease being cancelled.
- Repairs and maintenance are the responsibility of the firm that owns the asset.
- Leasing may be more expensive than buying the assets outright but it improves short-term liquidity.
Medium-term bank loans
These are bank loans with repayment terms of between one and five years.

Sources of long term finance
The long term finance denotes a time period of over five years. The two main choices are debt or share (equity) finance. Sources of long-term external debt finance include:
- loan capital/long-term bank loans
- share capital/equity finance
- government grants and subsidies
- venture capital
Loan capital/long-term bank loans
Loan capital borrowed from a bank is subject to regular interest payment. Interest can be variable or fixed. Variable interest rates offer less certainty as the percentage interest rate varies with the government base rate.
SECURITY
Loans can be secured or unsecured. A mortgage is a loan to buy property, secured against that property. The lender can reclaim the property used for security if the firm cannot keep up with repayments.
Share capital/equity finance
Limited companies issue shares to raise finance. They state their maximum authorized share capital in their Memorandum of Association. The value of the shares is shown in a company’s balance sheet.
RESTRICTIONS TO PVT LTD COMPANIES
Private limited companies (‘Ltd’) are not allowed to sell shares to the general public and are restricted to raising finance from private sources, often family and friends.
CAPITAL AND LIQUIDATION
Share capital is permanent capital because the funds are never paid back unless the company goes into voluntary liquidation. Unlike loans, share capital has no interest payments, so helping liquidity. The reward for holding shares is dividend payments based on a firm’s profits decided by the directors. In a bad year, a firm may not pay a dividend.
Additional sources of long-term finance
Governments at local, central or perhaps even supra-national (e.g. European Union) level will sometimes provide financial assistance in the form of aid, grants and subsidies, sometimes with artificially low interest rates. Grants may be given to firms if they are relocating or expanding in economically depressed areas.
Venture capital/industrial specialist
Specialist organizations provide funds for risky commercial ventures that banks refuse to finance. These include venture for which capitalists look for high returns. Venture capital is often used in management buyouts. Business angels are rich individuals prepared to put their money into business start-ups. They may work in syndicates, by taking a minority shareholding in return for their investment.
EQUITY STAKE
Venture capital is suitable only for entrepreneurial businesses, as owners have to part with an equity stake. There is no commitment to regular interest payments and the equity finance reduces gearing ratio. The venture capitalist offers management skills and advice.
Subsidies
Subsidies are government benefits in the form of cash or tax reductions. They grant to help the business or industry, such as farming, keeping the price of a commodity or service low, keeping the firm in business and preserving jobs.
References











I have read your article carefully and I agree with you very much. This has provided a great help for my thesis writing, and I will seriously improve it. However, I don’t know much about a certain place. Can you help me?